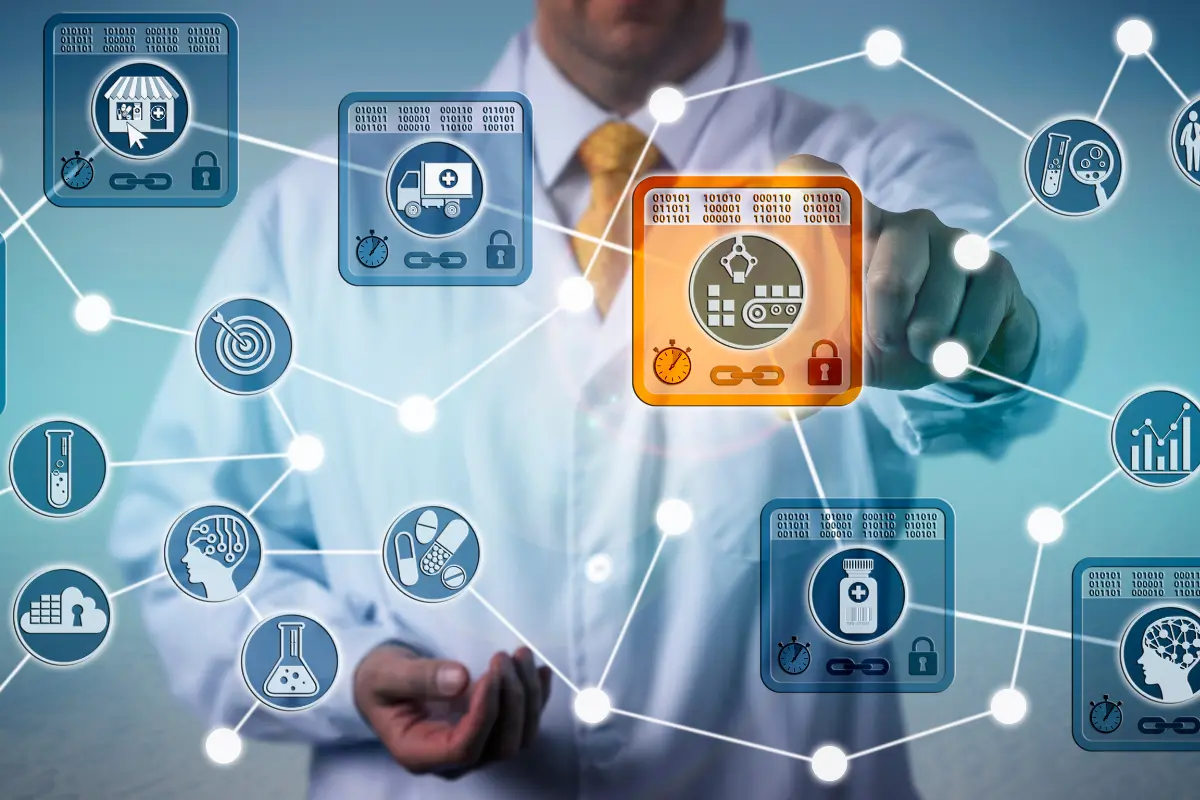
In an era defined by technological progress, the convergence of blockchain technology and manufacturing processes holds immense potential. Blockchain, a decentralized ledger, promises to revolutionize efficiency and transparency in manufacturing.
This article explores the intricacies, delving into blockchain fundamentals, the current manufacturing landscape, and the imperative for transparency. Amidst this transformation, the importance of empowering individuals in finance is highlighted.
For instance, Go immediate-vortex.com, an investment education firm, prioritizes knowledge over potential gains. This aligns with the theme of transparency explored in blockchain’s manufacturing context.
As technology evolves, so will blockchain solutions, necessitating adaptability for manufacturers to thrive. Despite challenges, embracing blockchain signals a transparent, efficient future for manufacturing.
Understanding Blockchain Technology in Manufacturing
Fundamentals of Blockchain
Blockchain operates on the principles of decentralization and a distributed ledger. Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain ensures that data is stored across a network of computers, promoting transparency and reducing the risk of manipulation. The immutable nature of blockchain records guarantees the integrity of manufacturing data.
Smart Contracts: Automating Processes in Manufacturing
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, play a pivotal role in automating various manufacturing processes. These contracts facilitate trust between parties and streamline transactions by eliminating intermediaries.
Security Features of Blockchain in Manufacturing
Blockchain’s inherent security features, including cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms, fortify the manufacturing ecosystem against data breaches and unauthorized access. This creates a tamper-resistant environment crucial for safeguarding sensitive manufacturing information.
Applications of Blockchain in the Manufacturing Industry
Supply Chain Traceability and Provenance
- Ensuring Raw Material Authenticity – Blockchain enables the transparent tracking of raw materials from their origin to the manufacturing facility. This ensures the authenticity of inputs, reducing the risk of counterfeit materials entering the supply chain.
- Tracking Manufacturing Processes – Through blockchain, every step in the manufacturing process can be recorded and verified in real-time. This level of transparency enhances accountability and traceability, crucial factors in maintaining product quality.
Quality Control and Compliance
- Improving Product Quality Assurance – Blockchain’s immutable ledger is instrumental in maintaining a comprehensive record of quality control measures throughout the manufacturing lifecycle. This not only ensures the consistency of product quality but also aids in identifying and rectifying issues promptly.
- Meeting Regulatory Standards through Transparency – Manufacturers face an array of regulatory standards. Blockchain’s transparent and auditable nature facilitates compliance, reducing the risk of regulatory violations and associated penalties.
Enhancing Collaboration through Blockchain
Interoperability in Manufacturing Ecosystems
Blockchain promotes interoperability, allowing seamless communication and data sharing among disparate systems within the manufacturing ecosystem. This interoperability fosters collaboration and accelerates decision-making processes.
Real-time Data Sharing among Stakeholders
Blockchain’s real-time data sharing capabilities empower stakeholders with immediate access to critical information. This ensures that decisions are based on the most current and accurate data, reducing delays in production processes.
Reducing Information Asymmetry in the Supply Chain
Eliminating information asymmetry is pivotal in fostering trust among stakeholders. Blockchain achieves this by providing a shared, transparent ledger accessible to all authorized participants, reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings and disputes.
Cost Reduction and Operational Efficiency
Streamlining Transactions and Payments
Blockchain’s ability to execute and enforce smart contracts expedites transactions, reducing the time and costs associated with traditional payment processes. This streamlined approach enhances cash flow and liquidity for manufacturers.
Minimizing Counterfeit Products and Fraud
The transparency provided by blockchain significantly mitigates the risks associated with counterfeit products and fraud. Manufacturers can verify the authenticity of products at every stage, instilling confidence in both consumers and stakeholders.
Optimizing Inventory Management with Blockchain
Blockchain’s real-time visibility into the supply chain enables manufacturers to optimize inventory management. Accurate and timely information about stock levels and demand fluctuations helps in minimizing excess inventory and associated holding costs.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Blockchain
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating blockchain with legacy systems poses challenges, requiring careful planning and execution. Compatibility issues may arise, necessitating a phased approach to implementation to minimize disruptions.
Privacy and Data Governance Concerns
The transparency that makes blockchain advantageous also raises concerns regarding data privacy. Striking the right balance between transparency and privacy is crucial, requiring robust data governance frameworks.
Scalability and Performance Issues
As manufacturing operations scale, the performance and scalability of blockchain networks become critical. Addressing these challenges requires continuous optimization and potentially exploring advanced consensus mechanisms.
Future Trends and Trends in Blockchain for Manufacturing
Integration with IoT and Industry 4.0
The integration of blockchain with the Internet of Things (IoT) enhances real-time data exchange, providing manufacturers with unprecedented insights into machine performance, predictive maintenance, and overall operational efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics in Manufacturing Blockchains
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain unlocks new possibilities in predictive analytics. Manufacturers can leverage AI algorithms to analyze blockchain data, optimizing production processes and resource allocation.
The Role of Blockchain in Sustainable and Eco-friendly Manufacturing Practices
Blockchain can contribute to sustainable manufacturing by transparently tracking and verifying the environmental impact of production processes. This supports eco-friendly initiatives and helps manufacturers adhere to sustainability goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology offers unparalleled advantages to the manufacturing sector, revolutionizing operations by bolstering traceability and transparency in the supply chain, automating processes, and diminishing operational costs.
As technology undergoes continuous evolution, so does the realm of blockchain solutions in manufacturing. This dynamic landscape demands persistent adaptation to emerging trends, ensuring manufacturers remain at the forefront of technological advancements.
Despite existing challenges, the substantial rewards of embracing blockchain in manufacturing underscore the necessity for widespread industry adoption and collaborative efforts. This collective commitment will undoubtedly pave the way for a future characterized by transparency, efficiency, and technological sophistication in manufacturing processes.

![Dogecoin Price Prediction 2050 [Updated] 3 Dogecoin price prediction 2050](https://knowworldnow.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Dogecoin-price-prediction-2050.webp)
![SafeMoon Price Prediction 2023, 2025, 2030, 2040, 2050 [Updated] 4 SafeMoon Price Prediction 2023, 2025, 2030, 2040, 2050](https://knowworldnow.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/SafeMoon-Price-Prediction-2023-2025-2030-2040-2050.png.webp)

