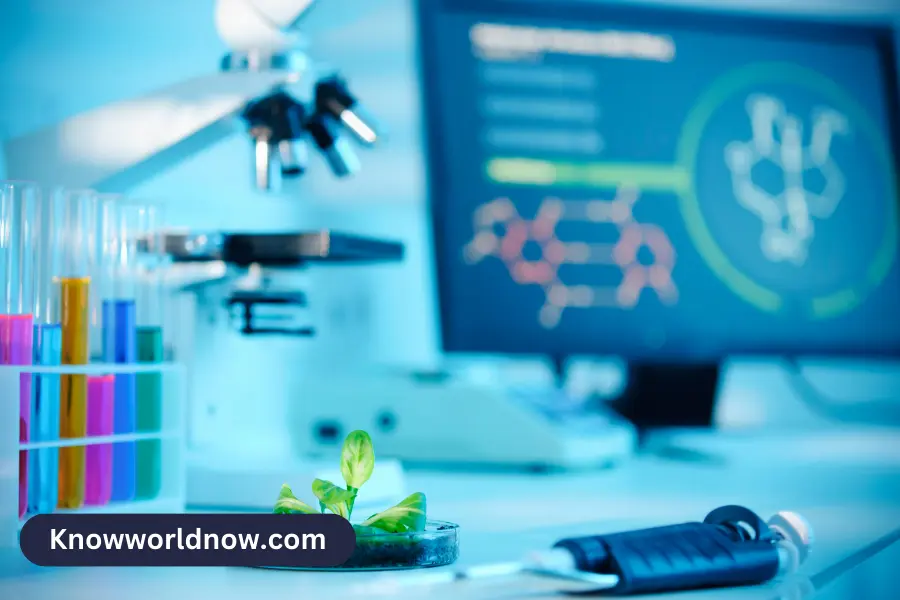
Refrigerated and BOD incubators provide a controlled environment for growing and storing cell cultures, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. Choose an incubator based on your lab’s needs.
Most refrigerated models utilize a compressor to lower the internal chamber temperature. These models can maintain temperatures up to 40 degrees cooler than ambient conditions for fermentation studies and Drosophila germination.
Advantages of a Refrigerated Incubator
A refrigerated incubator provides a controlled environment for various lab activities. Typical applications include bacterial culture, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) analysis, and plant growth studies.
They also come with multiple features that make them easier to use. Several models have exterior digital displays that are easy to read and manage, while others feature glass door panels that allow personnel to monitor contents inside constantly.
If you purchase a refrigerated incubator, check that it has good vibration protection and is easy to clean.
Refrigerated incubators are an excellent choice for many scientific research applications. They provide precise temperature control and can be used for forced degradation of antibiotics, protein crystal growth, and other scientific processes that require consistent temperature performance.
They are also ideal for research that needs to stably hold a temperature near room temperature, such as water pollution testing or bacteria research.
These incubators are available in various sizes to accommodate your specific needs. These incubators have an air jacket that regulates the internal temperature of the chamber.
This system provides rapid and precise temperature control, prevents evaporator-related drying out of samples, eliminates ice buildup, and reduces dehumidification during operation.
What is a BOD Incubator?
A BOD incubator, or biological oxygen demand incubator, is a type of laboratory equipment used to measure the amount of oxygen microorganisms consume while breaking down organic matter.
It is typically used in wastewater treatment plants and environmental laboratories to assess the quality of water and the efficiency of treatment processes.
A biological oxygen demand incubator is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment that continuously measures the amount of oxygen microorganisms consume.
It is commonly used in wastewater treatment plants and environmental laboratories to monitor the level of organic matter in water. Biochemical oxygen demand incubators are used in many molecular biology, microbiology, and biology cell investigations.
These devices are utilized to create and maintain bacterial or cell cultures, test tissue culture growth, and carry out BOD tests, among other things.
Difference Between a Refrigerated and a BOD Incubator
In the laboratory, there are two main types of incubators. They are Bacteriological incubators and BOD incubators. Incubators grow bacteria, yeast, molds, and other microbial cultures.
They also are commonly used for a variety of tests and research. Temperature is one of the essential differences between refrigerated and BOD incubators.
A standard incubator only offers heating options, while a BOD incubator provides both. A typical incubator operates at 37deg Celsius, and a BOD incubator runs at lower temperatures.
A standard incubator’s temperature is maintained through the compatible operation of the three major components, the temperature sensor, temperature controller, and temperature contactor.
Unlike an ordinary incubator, a BOD incubator sets its temperature with an advanced PID temperature regulator.



![F95Zone Games - The Ultimate Guide for 2021 [F95Z Guide] 5 F95Zone Games](https://knowworldnow.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/ArTtW5LrK3b-z-0-y-637f48d86203817a9042a857.webp)